As fast and wide as the PCI bus was, there was one task that threatened to consume all its bandwidth: displaying graphics. Early in the era of the ISA bus, monitors were driven by simple Monochrome Display adapter (MDA) and Colour Graphics Array (CGA) cards. A CGA graphics display could show four colours (two bits of data) at 320 by 200 pixels screen resolution at 60Hz, which required 128,000 bits of data per screen, or just over 937 KBps. An XGA image at a 16-bit colour depth requires 1.5MB of data for every image, and at a vertical refresh rate of 75Hz, this amount of data is required 75 times each second. Thanks to modern graphics adapters, not all of this data has to be transferred across the expansion bus, but 3D imaging technology created new problems.
- Agp Slot Definition And Function Definitions
- Agp Slot Definition And Function Examples
- Agp Slot Definition And Functions
The function aGP.R is a prototype R-only version for debugging and transparency purposes. It is slower than aGP, which is primarily in C. However it may be useful for developing new programs that involve similar subroutines. Note that aGP.R may provide different output than aGP due to differing library subroutines deployed in R and C. No AGP slot Video graphics. Realtek ALC880 8-channel High Definition Audio CODEC. In 4-channel, 6-channel, and 8-channel mode, the function of this port.
3D graphics have made it possible to model both fantastic and realistic worlds on-screen in enormous detail. Texture mapping and object hiding require huge amounts of data, and the graphics adapter needs to have fast access to this data to avoid the
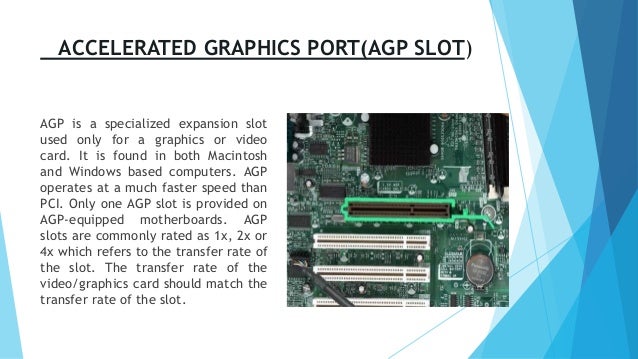
AGP operates at the speed of the processor bus, now known as the frontside bus. At a clock rate of 66MHz this is double the PCI clock speed and means that the peak base throughput is 264 MBps.
For graphics cards specifically designed to support it, AGP allows data to be sent during both the up and down clock cycle, doubling the clock rate to 133MHz and peak transfer to 528 MBps. This is known as 2x. To improve the length of time that AGP can maintain this peak transfer, the bus supports pipelining, which is another improvement over PCI. A pipelining 2x graphics card will be able to sustain throughput at 80% of the peak. AGP also supports queuing of up to 32 commands via a process called Sideband Addressing (SBA), the commands being sent while data is being received. This allows the bus to sustain peak performance for 95% of the time, according to Intel.
AGP’s four-fold bandwidth improvement and graphics-only nature ensures that large transfers of 3D graphics data don’t slow up the action on screen; nor will graphics data transfers be interrupted by other PCI devices. Being primarily intended to boost 3D performance, AGP also provides other improvements that are specifically aimed at this function.
With its increased access speed to system memory over the PCI bus, AGP can use system memory as if it’s actually on the graphics card. This is called Direct Memory Execute (DIME). A device called a Graphics Aperture Remapping Table (GART) handles the RAM addresses so that they can be distributed in small chunks throughout system memory rather than hijacking one large section, and presents them to a DIME-enabled graphics card as if they’re part of on-board memory. The main use for DIME is to allow much larger textures to be used because the graphics card can have a much larger memory space in which to load the DRDRAM) in the second half of 1999. AGP 2.0 was supported by chipsets launched early in 1999 to provide support for Intel’s Katmai processor.
AGP Pro is a physical specification aimed at satisfying the needs of high-end graphics card manufacturers, who are currently limited by the maximum electrical power that can be drawn by an AGP card (about 25W). AGP Pro caters for cards that draw up to 100W, and will use a slightly longer AGP slot that will also take current AGP cards.
DEFINITION, HISTORY,FUNCTION, SORTS AND DAMAGE OF MOTHERBOARD
CHAPTER IINTRODUCTIONv GENERAL
In the use of computers there are3 components involved in intense, thatare hardware (hardware), software (software), and brainware (human).There are no computer systems and computingactivities that do not involve all three components.
One is the hardware thatconsists of several components. This one isvery vital component tothe computer. Processors, graphics cards,harddisk and other devices on the computer will not work withoutit, the name is motherboard.
Our purpose in discussing this matter is to find components thatare part of a specific motherboard to the laymen.
v OBJECTIVES OF THIS WRITE
ü To explain history of motherboard
ü To explain the function of motherboard
CHAPTER II
The motherboard is the central printed circuit board,called Motherboard because this component is a majorcomponent of the series of CPUs, so the motherboard can beinterpreted in the Indonesian language isthe Parent Board or the main board.
As the name implies, themotherboard or mainboard is often also referredto the circuit board where all the other components areconnected. The motherboard is the control center that regulates the workof all the components installed. Regulate the provision of electrical power onany PC component. There were many small pieces slot to plugin RAM(Random Access Memory) andthe adapter. There plugged processors.
The motherboard is sometimes alternatively known as themainboard, system board, planar board or, on Apple computers, the logicboard. It is also sometimes casually shortened to mobo.
As the time gone, the motherboard has avariety of development accompanied by development of itscomponents. Where development will be very influence the mechanism ofother devices.
B. HISTORY OF MOTHERBOARD
Prior to the advent of the microprocessor, a computer wasusually built in a card-cage case or mainframe with components connected by abackplane consisting of a set of slots themselves connected with wires; in veryold designs the wires were discrete connections between card connector pins,but printed circuit boards soon became the standard practice.
The Central Processing Unit, memory and peripherals werehoused on individual printed circuit boards which plugged into the backplate.During the late 1980s and 1990s, it became economical to move an increasingnumber of peripheral functions onto the motherboard. In the late 1980s,motherboards began to include single ICs (called Super I/O chips) capable ofsupporting a set of low-speed peripherals: keyboard, mouse, floppy disk drive,serial ports, and parallel ports. As of the late 1990s, many personal computermotherboards supported a full range of audio, video, storage, and networkingfunctions without the need for any expansion cards at all; higher-end systemsfor 3D gaming and computer graphics typically retained only the graphics cardas a separate component.
The early pioneers of motherboard manufacturing wereMicronics, Mylex, AMI, DTK, Hauppauge, Orchid Technology, Elitegroup, DFI, anda number of Taiwan-based manufacturers.
The most popular computers such as the Apple II and IBM PChad published schematic diagrams and other documentation which permitted rapidreverse-engineering and third-party replacement motherboards. Usually intendedfor building new computers compatible with the exemplars, many motherboardsoffered additional performance or other features and were used to upgrade themanufacturer's original equipment.
Motherboard distinguished on theform and layout of the circuit is commonly calledthe form factor. From its shape, the motherboard areusually divided into two, namely the modelof desktop (monitorplaced on the CPU) and the model tower (monitor placed nextto theCPU).
While based on the form factors are used,the motherboarddistinguished on two biggroups: ATX (Advanced Technology -introduced by IBM in1984) and non ATX.
Modern motherboards include :
· Microprocessor or processor is a chip that serves as the brains of a PC.
· Power Connector is a pin which connect the motherboard with power supplyin casing of a computer
· chipsetwhich forms an interface between the CPU's front-side bus, main memory, andperipheral buses
· a clockgenerator which produces the system clock signal to synchronize the variouscomponents
Under the southbridge chipset heatsink that there arefunctions to perform input and output regulation of several components such ashard drives, optical drives, USB ports, and PCI Express expansion slots. Alongwith the many demands of the process to be done, so now it comes with thechipset heatsink to be more stable.
Located under the Chipset heatsink fan is equipped withworking with the southbridge chipset to make arrangements for a video card,processor, and memory. At this chipset has several new features that candeliver high speed ports for LAN connections and added extra PCI Express.
· Soket andslot of processor to plug your processor
· Floppy andIDE connector to connect the motherboard with storage devices
· StandbyPower LED as reminder for turn off the system power before turn onor turn off the machine.
· non-volatile memory chips (usually Flash ROM in modern motherboards) containingthe system's firmware or BIOS

· PS/2 MousePort
Agp Slot Definition And Function Definitions
· RJ-45 Port

· Microphonejack
· USB 2.0port 3 dan port 4
· Keyboardconnector
· BIOS
When you first turn on the PC, the motherboard will boot andrun code that contains the Basic Input Ouput System (BIOS), BIOS will run sometests to prepare for all the hardware and then run the operating system. BIOSitself is stored in Flash RAM with a capacity of about 2-4 MB, and chanced uponthis example has two motherboard BIOS.
· Expansionslots
Some of the latest motherboards are now equipped with a mixof PCI and PCI Express expansion slot. As for the PCI Express there are usuallytwo types, namely PCI Express 16x that serves to replace the AGP and PCIExpress 1x slot is the smallest size and will be used as a substitute for theexisting PCI slot for modem support and some other input device.
Some motherboard manufacturers usually equip chipsetmotherboard with some optional, like the Silicon Image SATA RAID, FireWireController Texas Instruments, and two Broadcom Gigabit LAN controller. Somechipsets can be used to support the connectivity that requires a highertransfer rate.
The motherboard or mainboard is the board / main board wherethe main components such as microprocessors and memory (RAM, ROM, BIOS) chipalong with other controllers. There is also SLOT Expansion is the place to putthe cards additional functions to improve the facilities and capabilitiesrequired. Microprocessor mounted on the socket / slot corresponding to theshape and size of the microprocessor, such as socket 370, 470, LGA 775, socketA 462 (AMD), the socket slot I (Pentium 2 and 3). On the motherboard,microprocessor communicates with other components via a bus or data path. Thisbus has evolved from the bus 66, 100, 133, 200, 266, 333, 400, 500, 800 MHz.This development was to compensate for the microprocessor work faster.Expansion slot also experiencing growth. Usually table of diagram has beenincluded on the motherboard when you buy a CPU / Mainboard .Processor orCPU (central processing unit) has the function to read and interpretinstructions, does execution, and storing the results in memory. CPU data busthat is used has a 16.32 or 64 bit.
Various sorts of Motherboard :
b. VIA Motherboard
d. INTEL Motherboard
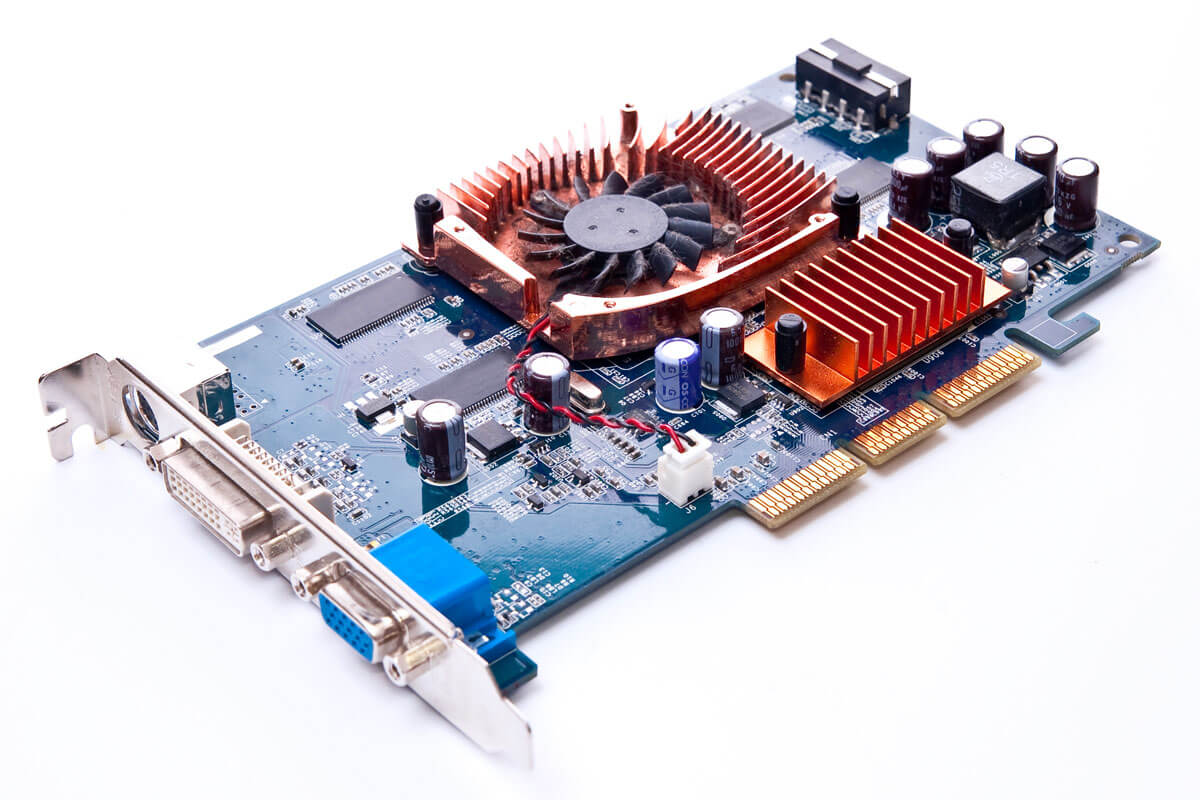
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/evga-geforce-6200-agp-graphics-card-amazon-56a6fade3df78cf772913fe9.png)
If the PC is often times show an attorney-alamatancomplicated, or displaying an error message, emits a continuous beep uniformlyor irregularly, the PC is probably in trouble,
This type of damage can be categorized into two categories :
Problems with hardware components need to be serious becauseof the difficulty of handling localized and removed without the proper tools,skills and experiences that support. Explanation will revolve around theproblems that often occur along with how to cope.
Symptoms:
Once turned on, no display on the monitor, the indicatorlight (LED) on the front panel is lit, the indicator light (LED) flashingmonitors, power supply fan and processor fan spins, no beep sound at the speaker.
The first step, loose all power cables which connected tothe electrical, data cable to the monitor, keyboard cable / mouse, and all thecables which connected to the CPU, then cashing out all the screw covers. In anopen case please also remove other components, ie the voltage of power supplycables are connected to the motherboard, hard drive, floppy, be careful not torush the process. So is the card attached to the Motherboard (VGA, Sound Cardor other). Now attached to the motherboard just cashing it. Please checkcarefully the motherboard, see Chip (IC), Elko, transistor and others if thereis a fire.
If there are no signs of burnt components likely motherboardis still good, but sometimes when motherboard does not work because of program damage which contained in the BIOS,
CHAPTER III
CONCLUSION
Agp Slot Definition And Function Examples
Based on the materials we havediscussed, we draw the following conclusion:
Agp Slot Definition And Functions
The motherboard is one component ofthe series of computer,componentsare called Motherborad because this component is amajor component of the series of CPUs, sothe motherboard can be interpreted in the Indonesianlanguage is the Parent Board or the main board which has slots for othercomponents, so that the components are connected to eachother and work together well.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/evga-geforce-6200-agp-graphics-card-amazon-56a6fade3df78cf772913fe9.png)
